Chondrus crispus—commonly called Irish moss or carrageen moss (Irish carraigín, “little rock”)—is a species of red algae which grows abundantly along the rocky parts of the Atlantic coast of Europe and North America. Chondrus crispus is an industrial source of carrageenan.
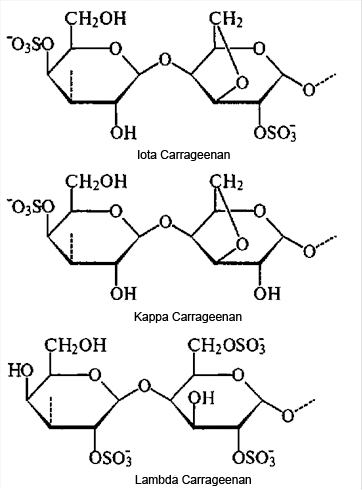
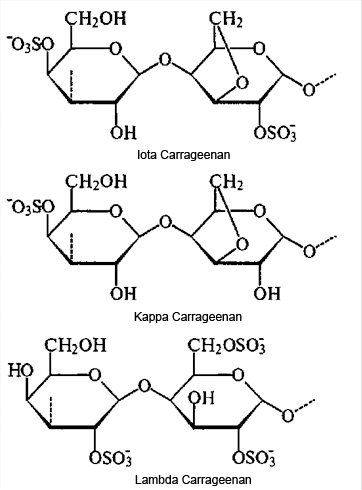
Carrageenans are a family of linear sulphated polysaccharides. All carrageenans are high-molecular-weight polysaccharides made up of repeating galactose units and 3,6 anhydrogalactose (3,6-AG), both sulfated and nonsulfated. The units are joined by alternating α-1,3 and β-1,4 glycosidic linkages. There are three main varieties of carrageenan, which differ in their degree of sulphation.
As explained by CP Kelco about its range on Carrageenan thickeners for personal care, by using the appropriate carrageenan product, the formulator can create textures ranging from free-flowing liquids to solid gels. Carrageenan products can be used to create rheological profiles ranging from free-flowing liquids to thixotropic liquid gels and self-supporting solid gels with a wide range of textures, setting temperatures and melting temperatures. With a single carrageenan product, a range of viscosities and gel strengths can be obtained by adjusting other ingredients in the formulation.
- Kappa carrageenan forms firm gels in the presence of ions.
- Iota carrageenan forms elastic gels and thixotropic fluids in the presence of ions.
- Lambda carrageenan forms viscous, non-gelling solutions.